
Many vegans and aspiring vegans care about eating a healthy, balanced diet and want to be well-informed about nutrition. Vegans have a significantly reduced risk for type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure and, on average, have lower cholesterol levels.
Although there are health benefits to being vegan, there are also nutrients to be aware of. We aim to give you all the essential information you need to know about vegan nutrition on this page. For those who want it, we provide links to additional information for each nutrient.
Page info by Jack Norris, registered dietitian and executive director of Vegan Outreach
“Where do you get your protein” is typically the first question vegans are asked. And it’s a bit hard to answer because all plant foods contain protein. In other words, vegans get our protein in everything we eat!
Eating a serving of high-protein plant foods at most meals will provide enough protein for most vegans (the exception being some strength athletes who should experiment with varying amounts to find the best results). Anyone who’s regularly been eating meat and cheese is used to high amounts of protein and if you’re craving animal products or feeling fatigued on a vegan diet, adding more protein is often the solution.

High-protein plant foods include seitan and most vegan meats (about 15-25 grams per serving, but check the label), tempeh (about 15 grams per 1/2 cup), tofu (about 10-15 grams per 1/2 cup), peanuts (about 15 grams per 1/2 cup), beans and lentils (about 8 grams per 1/2 cup), and soymilk (about 7 grams per cup).
If you want a thorough discussion about plant vs. animal protein, check out the article Protein Needs of Vegans from VeganHealth.org.

Speaking of protein, soy foods have traditionally been a staple of many vegan diets due to their high protein content. Myths abound that soy is harmful, and that has made some people shy away, but there’s plenty of scientific evidence that two servings of soyfoods per day is perfectly safe. Higher amounts are probably also safe, but they haven’t been studied as thoroughly.
The most robust area of research on soy has been with respect to breast cancer, and the overwhelming evidence is that soy can reduce the risk of breast cancer. There’s also evidence to suggest that soy can reduce the risk of prostate cancer and heart disease (by lowering LDL cholesterol). Soy: Main Controversies.
Tofu is an extremely versatile soyfood that has been eaten in some Asian cultures for hundreds of years and is very easily available in India. You can fry or bake it and add it to just about any savory dish. You can also freeze and then thaw it to give it a chewy texture. Tofu doesn’t have much taste on its own, but it takes on the flavors of the foods it’s mixed with.
Tofu is normally made with calcium salts and is therefore a rich source of calcium for vegans (check the packaging for “calcium” in the ingredients).
Another type of tofu, silken tofu, has a smooth texture and is used for making pudding, mousse, and cream-based pies. Silken tofu can be easily found in any nearby supermarket.
While most vegans eat soyfoods, you don’t need to in order to be a vegan as there are plenty of other high-protein foods. But unless you have a specific allergy to soy, there’s no reason why you can’t enjoy it just like millions of other people throughout the world, vegans and meat-eaters alike.
People often associate iron with red meat, so you might be surprised to know that iron is plentiful in plant foods and vegans often have higher iron intakes than meat-eaters. Obtaining enough iron from vegan foods is easy if you eat legumes (beans, peas, and lentils) and dark leafy green vegetables (such as spinach and amaranth). Iron is found in a range of other plant foods and many countries have foods fortified with iron. Blackstrap Jaggery (Kala Gud) is a type of jaggery that’s high in iron.

What’s more important for meeting iron needs as a vegan is to include foods high in vitamin C with meals which increases iron absorption from other foods at that meal. For example, oatmeal with orange juice at breakfast provides iron from the oats and vitamin C from the juice. The image below shows foods high in vitamin C and what amount should be eaten to significantly increase iron absorption.
Most vegans don’t need to be too concerned about iron unless they have a history of iron deficiency. One exception is long-distance runners who menstruate, as they have a high amount of red blood cell loss. If you’re prone to iron deficiency, eat plenty of meals containing foods high in iron and vitamin C and avoid coffee and tea (which decrease iron absorption) within an hour of such meals.
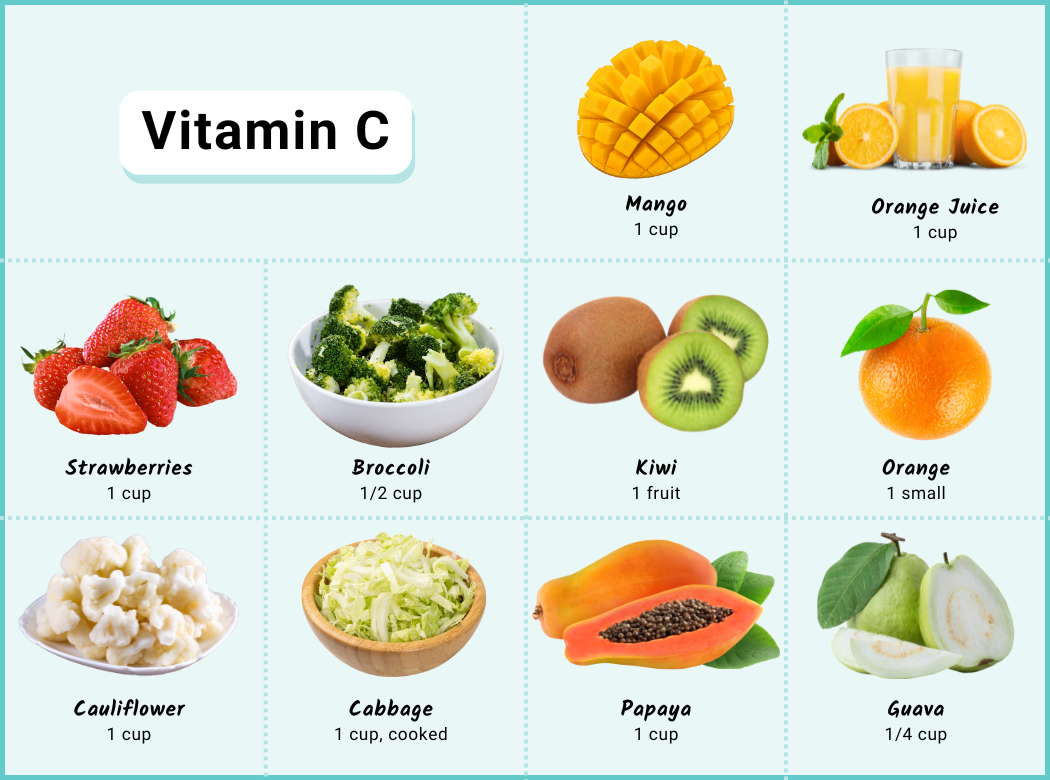
Most vegans don’t need to be too concerned about iron unless they have a history of iron deficiency. One exception is long-distance runners who menstruate, as they have a high amount of red blood cell loss. If you’re prone to iron deficiency, eat plenty of meals containing foods high in iron and vitamin C and avoid coffee and tea (which decrease iron absorption) within an hour of such meals.
Vegan adults should eat 3 servings of good sources of calcium per day while teenagers should eat 4 servings. The image below shows good sources of calcium that are readily available in India. The image lists the amount of each food that qualifies as one serving.
Luckily, most plant-based milks are fortified with calcium. And one of my favorite foods for obtaining calcium is tofu made with calcium salts, which is high in calcium and protein, both of which are good for bones. If you find it inconvenient to eat foods high in calcium each day, a calcium supplement of about 500 mg per day is another option.

Resistance exercise twice a week, involving lifting moderate weights, is possibly the most reliable way for people to increase the strength of their bones. We encourage everyone to follow such a program. Talk to your health professional about what program is right for you.

Vitamin A is important for night vision and bone density. Vegans should eat at least two servings of good sources daily. Good sources are vegetables and fruits whose edible flesh is orange: carrots and other root vegetables (1/2 cup), squash (1/2 cup), and melons (2 cups). The orange color indicates beta-carotene which our bodies can turn into vitamin A. Dark leafy green vegetables (1 cup cooked) are also high in vitamin A. Foods with yellow flesh are generally not good sources of vitamin A.
A great way to help satisfy your vitamin A needs is with Gajar Halwa!
Omega-3 fats are important for the long-term health of the heart and brain but are found in a limited number of plant foods. Walnuts, canola oil, flaxseeds and flaxseed oil, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and perilla oil are high in omega-3s.
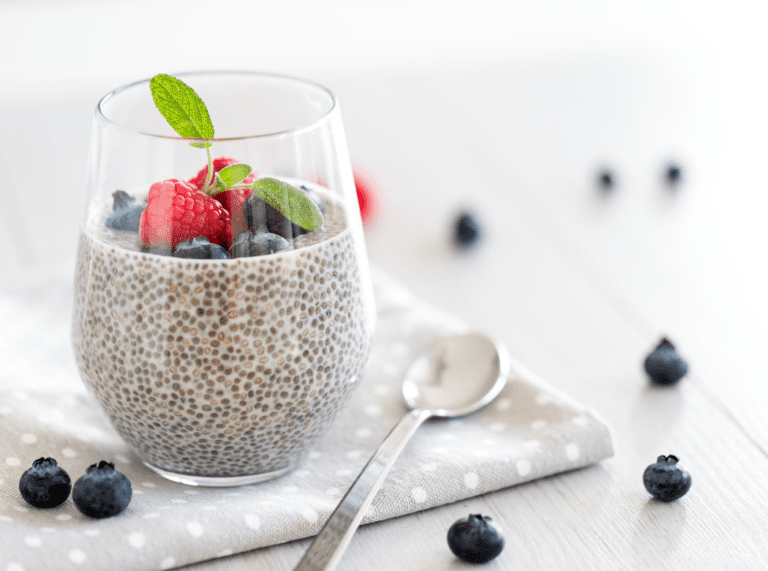
A delicious way to get your daily omega-3s is from Falooda (Chia Seed Pudding), which you can eat for breakfast or as a dessert.
Another option is to keep a jar of hemp or ground flaxseeds in the refrigerator to sprinkle them on meals throughout the day—they’re easy to incorporate into anything you’re eating.



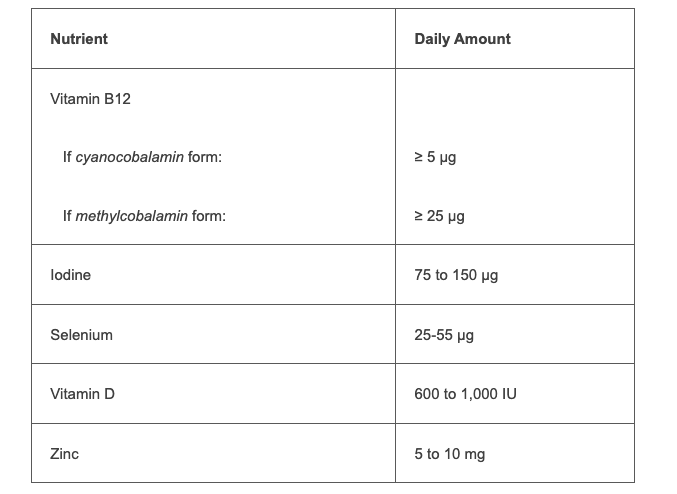
Nutrient deficiencies won’t occur in only a few weeks or even months of being vegan. That’s good news because it means you can go vegan at your own pace and worry about perfecting the nutrition later. In the long term, to be a thriving vegan, you’ll want to make sure you obtain a reliable source of vitamin B12, iodine, selenium, vitamin D, and in some cases zinc.


We recommend that vegans take a daily multivitamin that contains the amounts of nutrients listed in the table below. These amounts are not the recommended daily allowances (RDAs), but rather the amounts that will meet the needs of vegans after taking into account what vegans typically obtain through foods.
Good options for meeting these requirements are: